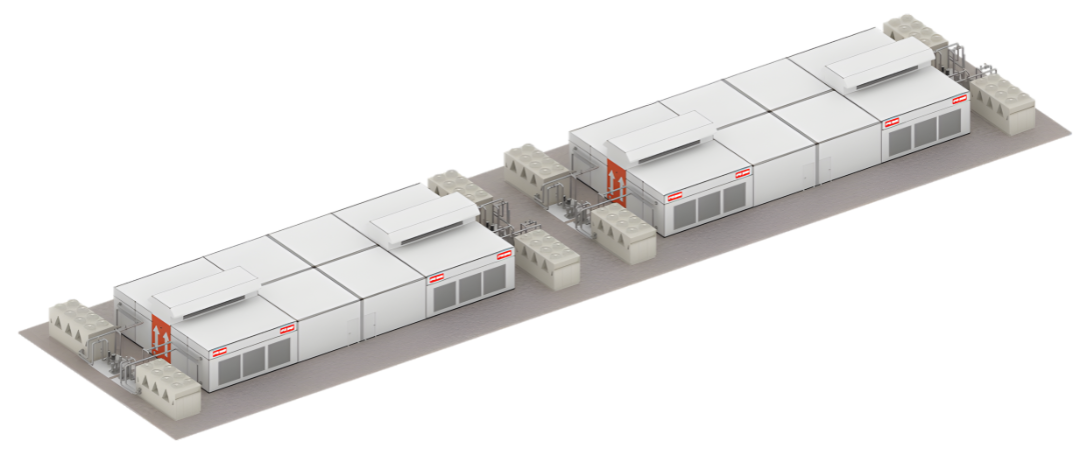
The Future of Modular Data Centers for AI Systems
By Daniel Robbins
Exploring the Benefits of Modular Data Centers for AI Systems and the Integration of Innovative Cooling Technologies Direct to Chip Liquid Cooling (DCLC) and Evaporative Air Cooling: Enhancing Performance, Efficiency, and Scalability of Modular Data Centers
The rapid expansion and growing demand for AI applications is placing significant strain on existing designs of data center infrastructure. Conventional cooling methods are proving inadequate in managing the heat generated by AI servers. Racks with a power capacity of 100kW + each cannot be feasibly accommodated in substantial numbers within an existing data center without resulting in significant unused space on the facility's data floor and a concomitant expenditure of excessive funds for the conversion of such space.
Most organization’s data centers that were designed before 2017 were built based on technologies that did not exist or were not commonplace. Result: Datacenters that were built only 7 years ago were not designed to support today’s High-Density Hardware requirements, much less tomorrow's constantly changing standards. Result: Datacenters that were built only 7 years ago were not designed to support today’s High-Density Hardware requirements, much less tomorrow's constantly changing standards.
Modular data centers offer a promising solution to the scalability and flexibility challenges faced by traditional data center designs Prefabricated units are designed for rapid deployment and can be easily scaled up or down to accommodate changing computational needs. Modular data centers provide a flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional brick-and-mortar facilities, making them ideal for AI applications with fluctuating workloads.
Introduction
NVIDIA, a leader in artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC), faces the challenge of managing the immense data processing and power consumption required by these advanced applications. Traditional data center cooling methods have proven inefficient, costly, and unsustainable. A promising solution is the Modular Data Center (MDC), which offers flexibility, scalability, and portability. This white paper explores how innovative cooling technologies like Direct to Chip Liquid Cooling (DCLC) and adiabatic cooling can enhance the performance, efficiency, and scalability of MDCs, thereby addressing the demanding requirements of AI Systems and HPC workloads.
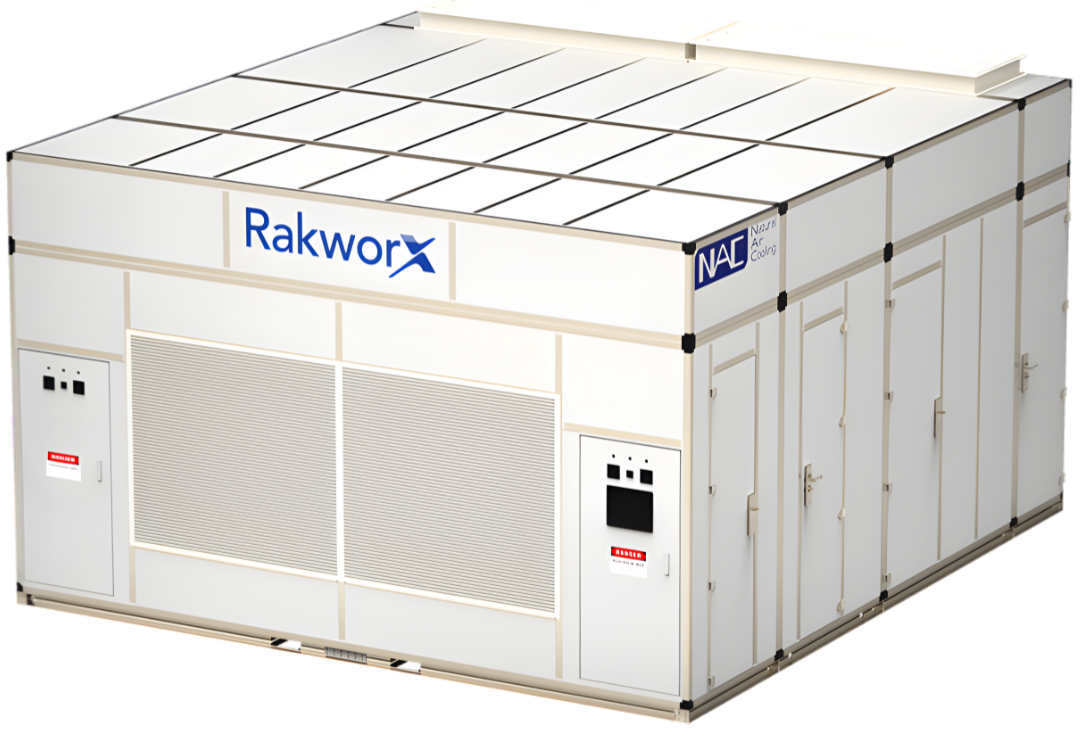
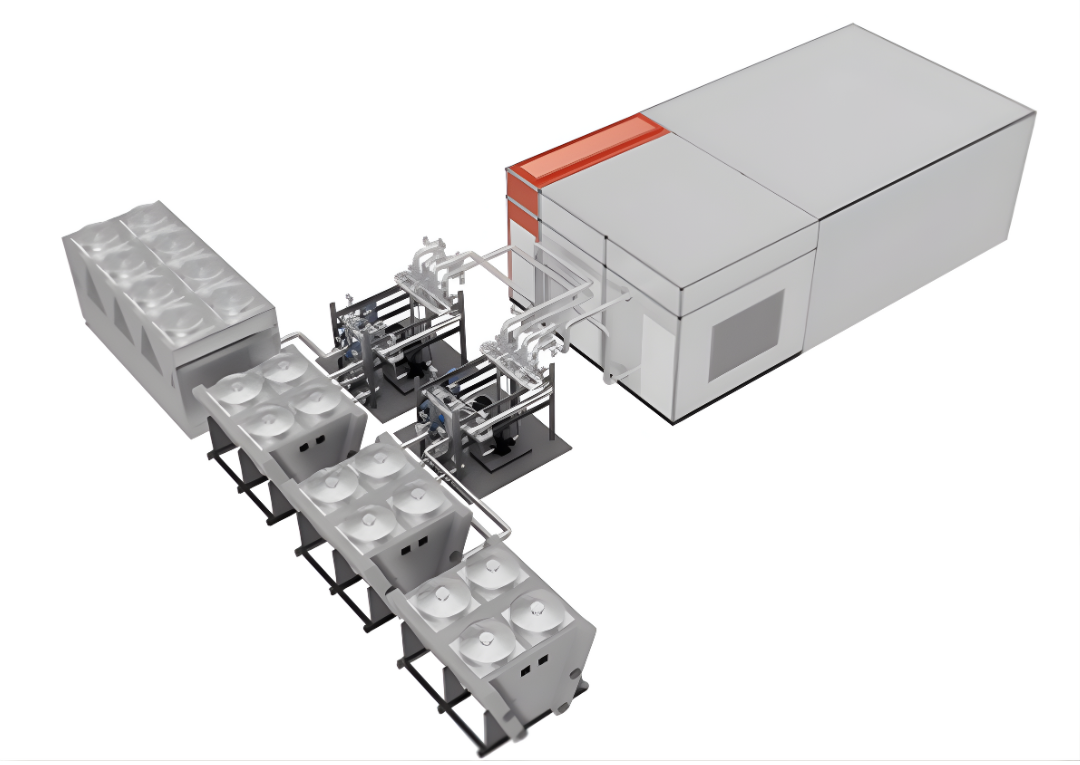
10 Rack MDC @ 130KW Per Rack Design with Vestibule
Modular Data Centers for AI Systems
Overview of MDCs
Modular Data Centers are prefabricated, self-contained, and standardized units designed for rapid deployment in various locations and environments. These MDCs are equipped to host NVIDIA's powerful AI platforms, including DGX, EGX, and HGX, which deliver unparalleled performance and scalability for AI and HPC tasks. By supporting NVIDIA's comprehensive AI software stack—such as CUDA, TensorRT, and RAPIDS—MDCs facilitate accelerated and optimized data processing and analytics.
Benefits of MDCs
1. Rapid Deployment: Significantly Reduced Construction Time Compared to Traditional Data Centers
One of the most compelling advantages of Modular Data Centers (MDCs) is their ability to be rapidly deployed, which is a critical factor in today's fast-paced technology landscape. Traditional data centers often require extensive site preparation, construction, and infrastructure development, which can take months or even years to complete. In contrast, MDCs are prefabricated in controlled environments, which allows for simultaneous construction and on-site preparation, dramatically reducing the overall deployment timeline.
Pre-fabrication Process: MDCs are built off-site in factories where environmental conditions are controlled, leading to higher quality and consistency. This also means that different modules can be manufactured concurrently, rather than sequentially as in traditional construction. Once completed, these modules are transported to the site and assembled, drastically cutting down the time required for site work.
Reduced On-site Construction: Since much of the work is done off-site, the need for on-site construction is minimized. This not only reduces the time needed to get the data center operational but also lowers the disruption to the site, whether it’s in an urban environment or a remote location. The modular approach allows for a faster setup of IT infrastructure, cooling systems, and power distribution.
Scalable and Flexible: MDCs can be scaled up or down quickly to meet changing needs. If more capacity is needed, additional modules can be added in a fraction of the time it would take to expand a traditional data center. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for organizations that need to respond quickly to increased demand, such as cloud service providers, research institutions, or companies expanding into new markets.
Expedited Workload Production: As a result of the rapid deployment of MDC’s, workload production can occur at an expedited pace. Most Brick and Morter data centers are unable to provide a conditioned environment prior to eighteen months after the commencement of construction. In many cases, MDC’s can be deployed in no more than half that amount of time.
2. Cost Efficiency: Lower Upfront Capital Expenditure and Operational Costs
Cost efficiency is a major driver for the adoption of MDCs. Traditional data centers require significant capital investment upfront, including costs for land acquisition, construction, and infrastructure setup. MDCs, however, offer a more economical alternative through their modular design and scalable architecture.
Lower Initial Capital Expenditure: The modular nature of MDCs allows organizations to start with only the capacity they need, reducing the need for large, upfront investments in infrastructure that may not be fully utilized for years. The pre-fabrication process also reduces material waste and labor costs, contributing to overall savings.
Pay-as-you-Grow Model: MDCs support a pay-as-you-grow approach, where organizations can invest in additional modules only when needed. This avoids the over-provisioning that is common in traditional data centers, where companies often build excess capacity to accommodate future growth. By aligning capital expenditure with actual demand, organizations can better manage their budgets and reduce financial risk.
Operational Cost Savings: MDCs are designed with energy efficiency and optimized cooling systems in mind, leading to lower operating costs. The integration of advanced cooling technologies such as Direct-to-Chip Liquid Cooling (DCLC) and hybrid systems not only reduces energy consumption but also extends the lifespan of equipment, further driving down maintenance and replacement costs. Additionally, the modular design allows for easier upgrades and maintenance, reducing downtime and associated costs.
3. Energy Efficiency: Integration of Innovative Cooling Technologies Reduces Energy Consumption
Energy efficiency is a critical concern for data centers, given their substantial power requirements and the growing emphasis on sustainability. MDCs address this challenge by integrating innovative cooling technologies that significantly reduce energy consumption while maintaining optimal operating conditions for high-performance computing.
Advanced Cooling Technologies: Traditional air-cooling systems are often inadequate for the high-density computing environments required by AI and HPC workloads. MDCs utilize advanced cooling methods such as Direct-to-Chip Liquid Cooling (DCLC), evaporative cooling, and hybrid systems that combine multiple cooling techniques. These systems are far more effective at dissipating heat from densely packed servers, reducing the need for energy-intensive air conditioning and lowering overall power usage.
Improved Thermal Management: Effective thermal management is essential for maintaining the performance and reliability of IT equipment. By directly cooling critical components like CPUs and GPUs, advanced cooling technologies minimize the risk of overheating, which can lead to thermal throttling and reduced performance. This not only ensures that data centers operate at peak efficiency but also extends the lifespan of the equipment, further contributing to energy savings.
Lower Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE): PUE is a key metric used to measure the energy efficiency of a data center, representing the ratio of total energy consumed by the data center to the energy used by IT equipment. MDCs with integrated advanced cooling technologies often achieve lower PUE values compared to traditional data centers, indicating more efficient use of energy. This not only reduces operational costs but also aligns with global sustainability goals.
4. Sustainability: Supports Heat Reuse and Reduces Environmental Impact
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the design and operation of data centers as organizations seek to minimize their environmental footprint. MDCs are well-suited to meet these sustainability goals through their support for heat reuse and their overall reduction in environmental impact.
Heat Reuse Capabilities: One of the most significant advantages of MDCs equipped with advanced cooling technologies is the potential for heat reuse. Systems like DCLC and hybrid cooling often generate waste heat, which can be captured and repurposed for other applications, such as heating office spaces, providing hot water, or even powering district heating systems. This not only improves the overall energy efficiency of the data center but also contributes to the sustainability of the surrounding community.
Reduced Carbon Footprint: MDCs are designed to be more energy-efficient than traditional data centers, consuming less power and reducing the need for energy-intensive cooling solutions. By optimizing energy use and integrating renewable energy sources where possible, MDCs help lower the carbon footprint associated with data center operations. This is increasingly important as organizations face pressure from stakeholders and regulators to meet stringent environmental standards.
Sustainable Design and Materials: The prefabricated nature of MDCs also contributes to their sustainability. The controlled environment in which they are built allows for the use of sustainable materials and construction practices that reduce waste. Additionally, the modular design enables efficient space utilization, reducing the need for large land areas and minimizing the impact on natural habitats.
Alignment with Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): For many organizations, the adoption of sustainable data center practices is a key component of their CSR strategy. MDCs not only help companies meet their sustainability goals but also enhance their reputation as environmentally responsible entities. This can lead to increased customer trust and potentially open new business opportunities in markets that prioritize sustainability.
Cooling Technologies in MDCs
1. Direct to Chip Liquid Cooling (DCLC)
Technology Description: Direct to Chip Liquid Cooling (DCLC) transfers heat directly from the chip to a liquid coolant—such as water or dielectric fluid—via a microchannel heat sink attached to the chip. This method significantly improves the thermal management of data centers.
Advantages of DCLC
Enhanced Performance: DCLC reduces chip temperatures, thereby increasing performance and extending the lifespan of the hardware. This is crucial for maintaining the high performance required by AI and HPC applications.
Energy Efficiency: By eliminating the need for traditional cooling mechanisms such as fans, air conditioners, and chillers, DCLC significantly reduces power consumption and noise levels in data centers.
Space Optimization: DCLC enables higher density and more compact MDC designs, resulting in a more flexible and efficient use of space within the data center.
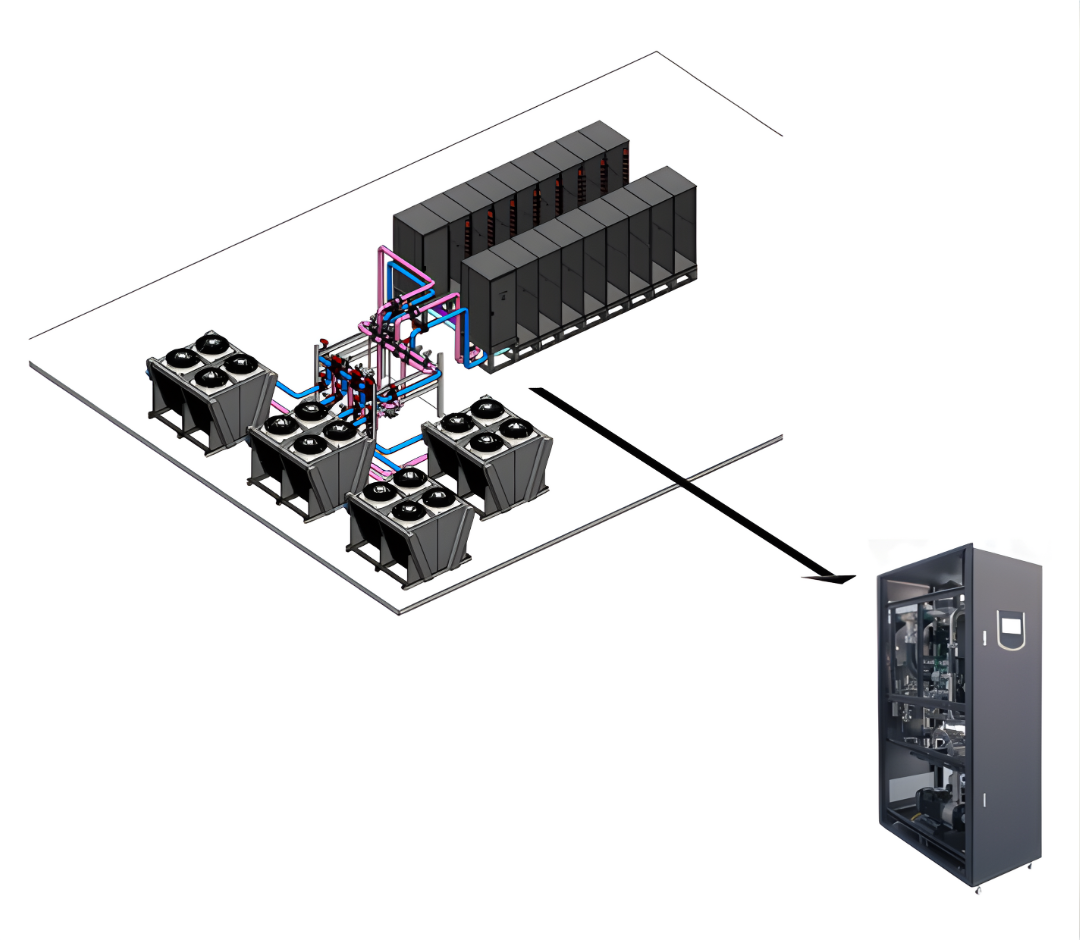
Cooling Distribution Unit (CDU)
2. Adiabatic Cooling for MDC’s
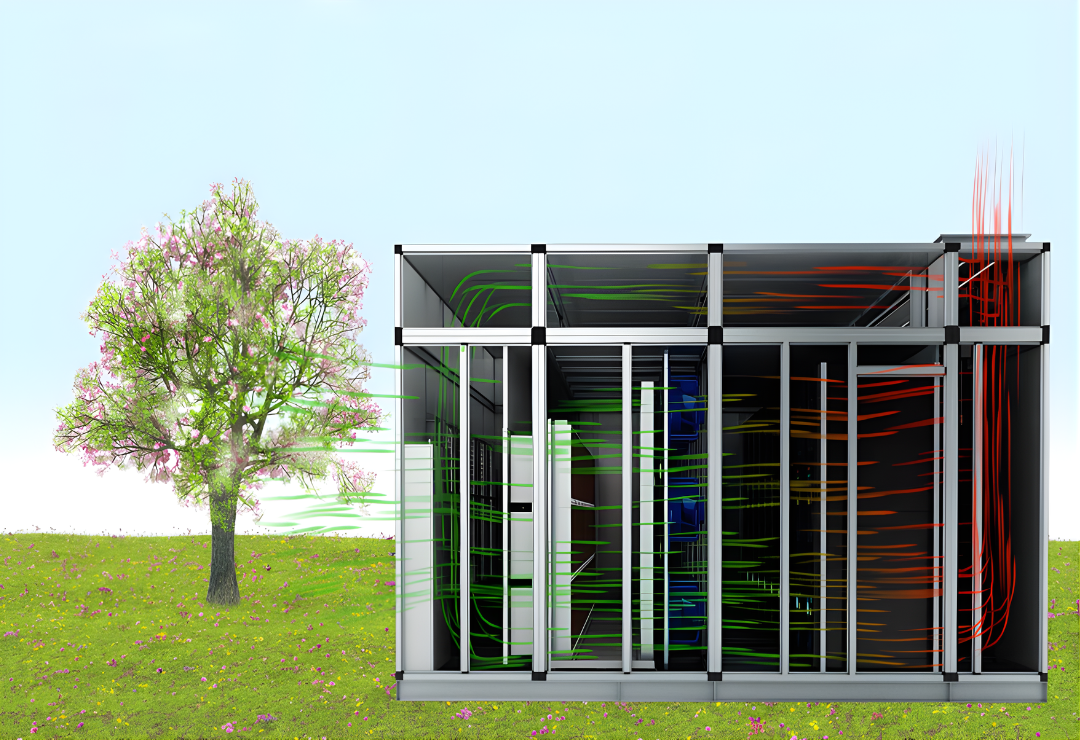
Technology Description: Adiabatic cooling utilizes the evaporation of water to cool the air without adding humidity. This process involves passing air through a wet saturated medium, where it cools down as water evaporates.
Advantages of Adiabatic Cooling
Improved Air Quality: Adiabatic cooling lowers the ambient temperature and increases airflow, thereby improving the overall air quality within the data center.
Sustainability: This cooling method reduces water consumption and the carbon footprint of data centers. Additionally, it decreases dependence on external water and power sources, making it a more sustainable and eco-friendly option.
Adaptability: Adiabatic cooling systems are more resilient to varying climates and seasons, making MDCs adaptable to different environmental conditions.
Adiabatic Cooling MDC System
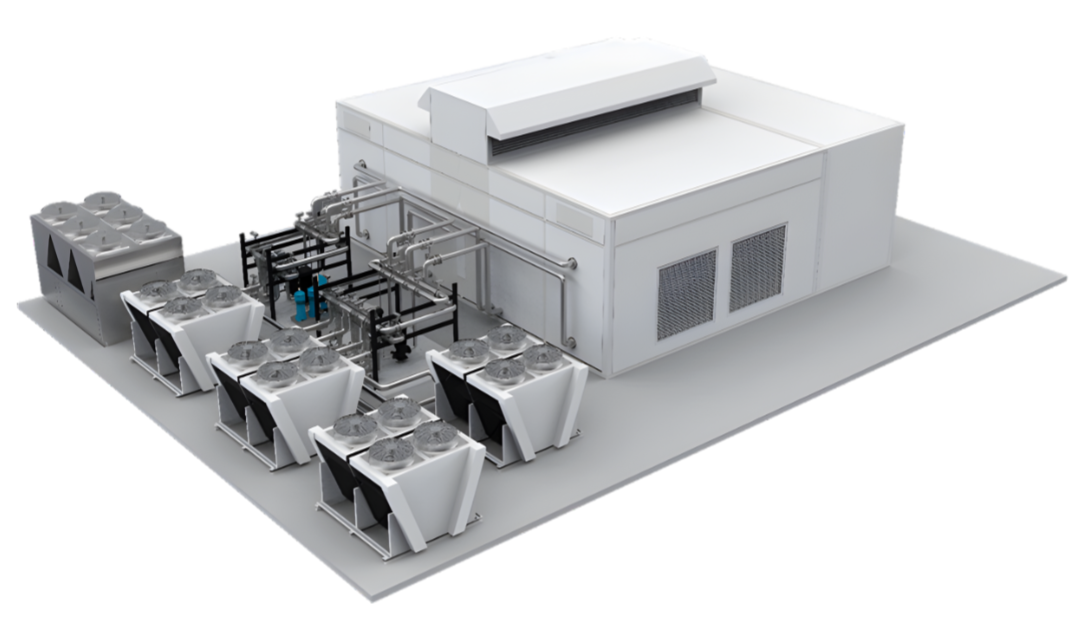
3. Hybrid Cooling Systems
Technology Description: Combines different cooling methods, such as evaporative cooling and DCLC, to manage the diverse heat profiles generated by AI workloads.
Advantages:
Flexibility in adapting to different environmental conditions and workload requirements.
Scalability to meet increasing computational demands.
Enhanced energy efficiency by optimizing cooling resource allocation.
20 Rack Hybrid MDC design with Vestibule
Application for AI and HPC
NVIDIA, a leader in AI and GPU technology, exemplifies the growing demand for advanced cooling solutions in MDCs. As AI workloads continue to intensify, the need for innovative cooling systems that can handle high thermal loads and ensure efficient operation becomes critical. The integration of DCLC and adiabatic cooling in MDCs ensures that NVIDIA’s GPUs operate at peak efficiency, thereby extending their lifespan and maintaining high performance.
Challenges and Solutions in Modular Data Centers
1. Technical Challenges:
The integration of advanced cooling systems in Modular Data Centers (MDCs) is a complex process, particularly when it involves hybrid cooling systems such as Direct-to-Chip Liquid Cooling (DCLC) and evaporative cooling. These systems are designed to handle high-density computing environments, but they come with several technical challenges that need to be addressed for optimal performance.
Integration of Hybrid Cooling Systems: Hybrid cooling solutions, which combine multiple cooling techniques (e.g., liquid cooling and air cooling), require careful design and specialized infrastructure. This includes the integration of various subsystems such as Coolant Distribution Units (CDUs), Door Heat Exchangers (HX), and liquid-cooling loops that must be designed to work in harmony. These systems must not only be efficient but also capable of scaling with growing computational demands. Ensuring that all components are properly integrated, and function seamlessly requires detailed engineering and design considerations to avoid system inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or downtime.
Infrastructure Complexity: The infrastructure needed to support hybrid cooling, especially in high-density AI or HPC environments, can be more complex than traditional cooling solutions. Hybrid systems often require dedicated cooling loops, specialized piping for liquid coolants, and advanced control mechanisms to manage different cooling loads. This can add to the complexity of both initial setup and ongoing maintenance, as specialized equipment and expertise are required to ensure optimal operation.
Maintenance Requirements: While advanced cooling systems significantly improve energy efficiency and performance, they also require regular monitoring and maintenance. Components such as pumps, coolant distribution units, and heat exchangers need to be regularly checked for efficiency, leaks, or wear. This maintenance necessitates skilled personnel who are trained in the specific nuances of hybrid and liquid cooling systems, and failure to perform proper maintenance can lead to operational inefficiencies, overheating, or equipment failure.
Solutions:
Comprehensive Planning and Expert Installation: To address these technical challenges, comprehensive planning during the design phase is critical. Detailed simulations and modeling can be used to predict system behavior and identify potential issues before installation. Engaging experts with experience in hybrid cooling and MDC design ensures that all components are correctly integrated, minimizing the risk of system failures. Vendors and consultants specializing in advanced cooling technologies can provide valuable insights into the design and installation process.
Automated Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance: Implementing automated monitoring systems can significantly reduce the burden of manual inspections. These systems use sensors and real-time analytics to continuously monitor the performance of cooling systems, detecting issues such as temperature fluctuations, coolant flow anomalies, or potential leaks. Automated alerts can prompt immediate action, preventing minor issues from escalating into major failures. Additionally, predictive maintenance techniques can be used to schedule servicing before components degrade, further enhancing system reliability.
2. Cost Considerations:
The cost of implementing advanced cooling technologies in MDCs can be a barrier for many organizations. Liquid cooling systems, hybrid solutions, and the necessary infrastructure often come with higher upfront costs compared to traditional air-cooling methods. However, the long-term benefits in terms of energy savings, reduced operational costs, and enhanced equipment lifespan often justify these initial investments.
High Initial Investment: The specialized equipment and infrastructure required for advanced cooling systems, such as liquid-cooled racks, hybrid cooling units, and control systems, typically demand significant upfront capital. For organizations with limited budgets, this can be a deterrent, particularly if they are unsure about the long-term returns on investment.
Long-Term Savings: Despite the high initial costs, advanced cooling systems are far more energy-efficient than traditional methods. By reducing the energy required for cooling, organizations can achieve significant cost savings over time. Additionally, these systems tend to improve the longevity of IT equipment by maintaining optimal operating temperatures, which reduces the frequency of repairs and replacements, further contributing to long-term savings.
Solutions:
Cost-Benefit Analysis and Financial Planning: Conducting a detailed cost-benefit analysis is essential to understanding the long-term financial benefits of advanced cooling systems. This analysis should take into account not only the upfront costs but also the projected savings in energy consumption, reduced maintenance, and extended equipment lifespan. This will provide a clear picture of the return on investment (ROI) and help organizations make informed decisions. In some cases, phased implementations can be considered, where the advanced cooling systems are gradually introduced to spread out the capital expenditure over time.
Phased Implementations: A phased approach allows organizations to implement advanced cooling technologies in stages, aligning capital investments with growing capacity needs. For example, a company might initially invest in hybrid cooling for its most critical or high-density workloads, and then expand the system as its computational demands increase. This approach reduces financial strain and ensures that the benefits of advanced cooling can be realized progressively.
3. Operational Challenges:
Managing and maintaining advanced cooling systems in MDCs require skilled personnel who are familiar with the unique requirements of hybrid cooling solutions. Organizations may face operational challenges related to training and knowledge gaps, particularly if they are transitioning from traditional data center cooling methods.
Training and Expertise: Advanced cooling systems like DCLC and hybrid solutions are more complex than conventional air-cooling systems. They require a deep understanding of fluid dynamics, thermal management, and the operation of control systems. Staff responsible for managing these systems must be trained to operate, monitor, and maintain the cooling infrastructure. In many cases, organizations may need to hire or train specialized personnel to handle the unique demands of these systems.
Vendor Support: In addition to internal training, organizations may need to rely on vendor support for the installation, operation, and maintenance of advanced cooling systems. Vendors often provide valuable resources, including maintenance contracts, support services, and updates to cooling system technologies.
Solutions:
Developing Robust Training Programs: Organizations should invest in comprehensive training programs for their data center staff to ensure they are equipped to manage the complexities of advanced cooling systems. These training programs should cover everything from routine maintenance to emergency response procedures. Regular refresher courses and certification programs can help staff stay up to date with the latest advancements in cooling technology. Training should also emphasize predictive maintenance and the use of automated monitoring systems, which can reduce the workload on personnel while improving system reliability.
Leveraging Vendor Support: Vendors can provide a wealth of knowledge and support when it comes to managing advanced cooling systems. Engaging with vendors for ongoing maintenance and operational support ensures that the systems are running optimally and that any issues are addressed promptly. Vendor training sessions and technical support contracts can also ensure that internal teams are continuously learning from experts, which helps bridge the skills gap and mitigate operational risks.
Future Outlook
As AI and HPC demands continue to grow, MDCs equipped with hybrid cooling systems are poised to become the standard for data center infrastructure. Future advancements may include further miniaturization of cooling systems, integration with renewable energy sources, and the development of more efficient coolants. The ongoing collaboration between industry leaders like NVIDIA and the broader tech community will drive the continuous improvement of MDC technologies, enabling new breakthroughs in AI and HPC applications.
160 Rack Hyperscale Rack MDC design with Vestibule
Conclusion
Nvidia is a pioneer and innovator in AI and HPC, and MDC is a promising and practical solution for its data center needs. DCLC and adiabatic cooling are cutting-edge technologies that can enhance the performance, efficiency, and scalability of MDCs, as well as the environmental and social benefits. AI Users can leverage DCLC and adiabatic cooling to create the future of MDCs for AI and HPC, and to deliver the best value and experience to its customers and partners.
Adiabatic cooling is an energy-efficient cooling solution that reduces the amount of electricity required to cool a data center. It uses less energy and reduces the carbon footprint of the data center. By reducing the amount of electricity required for cooling, adiabatic cooling can significantly reduce the operating costs of a data center. Adiabatic cooling is a more sustainable approach to data center management, as it uses less energy and reduces the carbon footprint of the data center
These innovations not only improve thermal management and energy efficiency but also contribute to environmental sustainability. As a result, NVIDIA can deliver superior value and experience to its customers and partners, solidifying its position at the forefront of the AI and HPC landscape.
While the integration of advanced cooling technologies into MDCs presents several challenges—technical, financial, and operational—there are clear solutions available. Comprehensive planning, cost-benefit analysis, phased implementation, and robust training programs, coupled with automated monitoring and vendor support, can mitigate these challenges and ensure the successful deployment and operation of hybrid cooling systems. These solutions will ultimately lead to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced sustainability for organizations adopting MDCs for their AI and HPC workloads.
Modular Data Centers represent a significant advancement in data center technology, offering a scalable, efficient, and sustainable solution to the growing demands of AI and HPC. By integrating advanced cooling technologies such as DCLC, adiabatic, and hybrid systems, MDCs can support the next generation of high-density computing environments while minimizing environmental impact. As the industry evolves, MDCs will play a crucial role in shaping the future of AI and HPC infrastructure.
Daniel Robbins
Executive Director, Modular Data Centers
RakworX
Serving the Data Center and Mission Critical industries for more than 15 years, RakworX manufactures and distributes computer server racks, power distribution units, electrical switchgear and modular data centers. It offers off-the-shelf as well as fully customized products to hundreds of customers around the nationally and internationally. It has deployed over 2,300 Megawatts of modular data centers in more than 15 countries.